Not all bites and stings are the same, as some species can cause more damage than others. However, people who have allergies might experience life-threatening symptoms that require emergency treatment.
This article gives you a general overview of insect bites and stings and how to treat them.
Insect Bites and Stings
The current estimate of insect species living in Australia is approximately 200,000, yet only 62,000 have been named and identified.
With these numbers, it is no surprise that everyone has experienced an insect bite or sting before.
Most bites and stings only cause minor irritation with are treatable at home. Although many people seem far more susceptible to these bites, some may experience spectacular and life-threatening reactions.
In fact, insect and spider bites result in more deaths than snakes. Most deaths are due to allergic reactions to the venom rather than the toxins itself.
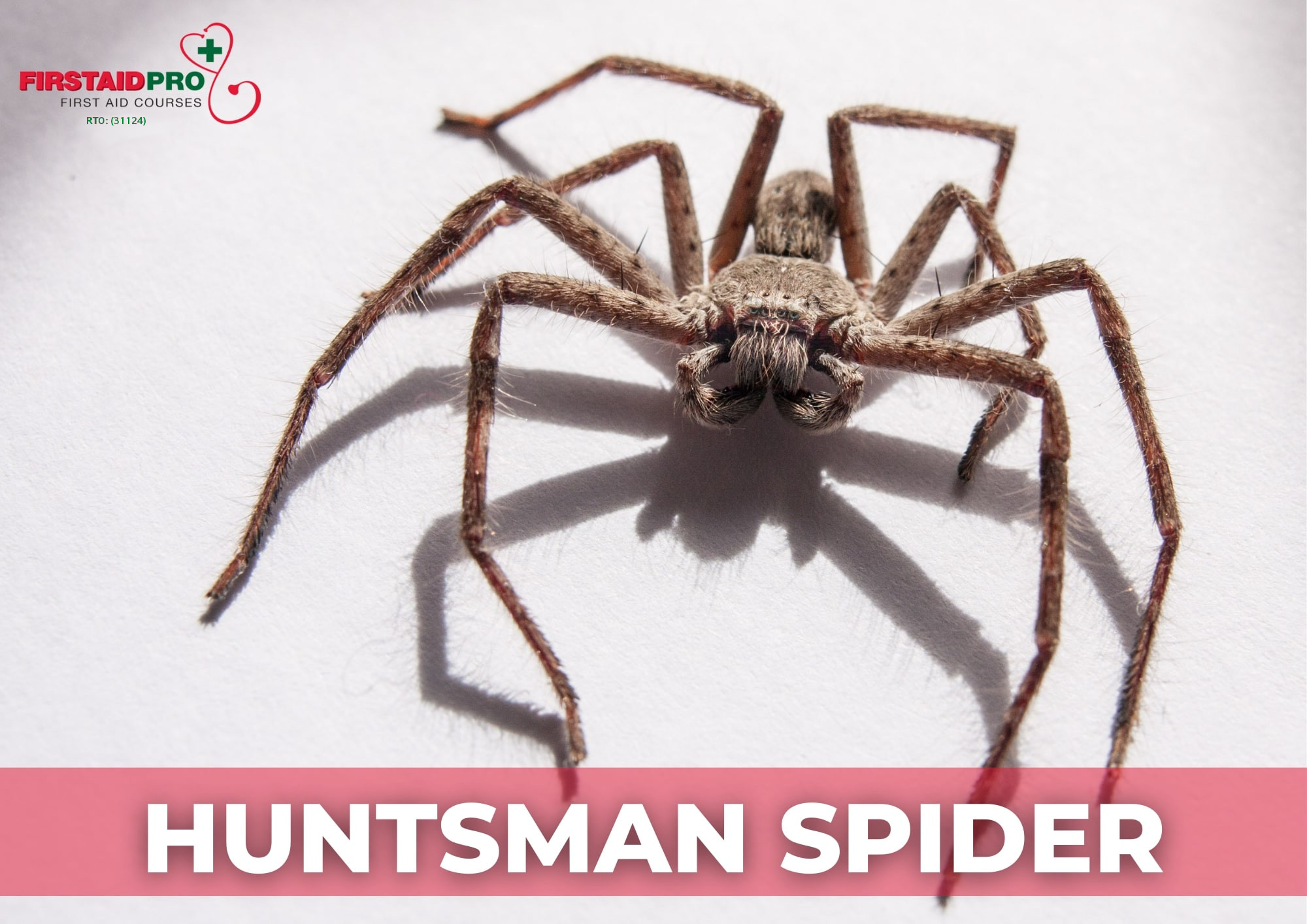
Certain spider bites, such as the redback spider and funnel-web spiders, can cause severe anaphylactic shock (anaphylaxis). If not treated, it can quickly result in rapid death.
Signs and Symptoms
Here are common symptoms of anaphylaxis from insect bites and stings.
- Abdominal pain or vomiting
- Chest pain
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty breathing
- Face or mouth swelling
- Fainting or lightheadedness
- Rash or skin flushing
First Aid for Insect Bites and Stings
Call emergency services
Call triple zero (000) if a person receives a large number of bites and stings in the mouth or throat. Emergency assistance is vital as this can result in shortness of breath or throat swelling, which can be fatal.
Remove the Stinger
Some insects (e.g., honeybees, yellow jackets) can leave a stinger on the skin. To remove the stinger, scrape the area with a fingernail or use a credit card.
Do not pinch the stinger using your fingers or tweezers. Doing so can only inject more venom onto the skin.
Clean the Area
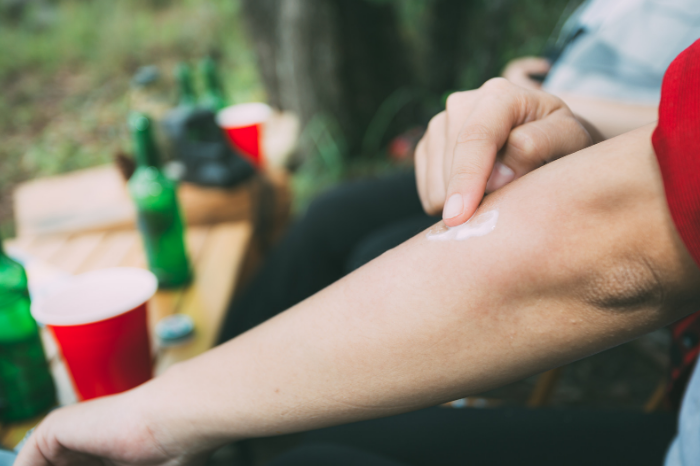
Gently wash the area using soap and clean water. Apply a cloth with cold water to further protect the skin.
Apply calamine lotion
Put calamine lotion on the area several times a day to help relieve pain and itchiness. Calamine lotion is a type of antihistamine cream best used in these scenarios.
Alternatively, you can use baking soda and water paste if calamine lotion is unavailable.
Treat Symptoms
There are several ways to treat bites and stings symptoms.
- Apply ice to the impacted area for about 10 minutes and rest simultaneously. Repeat the application a few times. Elevate the area if the bite or sting is on the arm or leg.
- If the pain becomes unbearable, take over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers such as acetaminophen or Ibuprofen. Be sure to follow the instructions on the recommended dosage found on the bottle. For small children, it is best to call a paediatrician for the next best steps.
- Remove any tight jewellery on the bitten area. These items can be hard to get off once that body part starts to swell.
Use an Epipen
If the person is responsive, ask if they are carrying an epinephrine auto-injector or EpiPen with them. If they do, retrieve it and help them use it according to the directions found on the label.
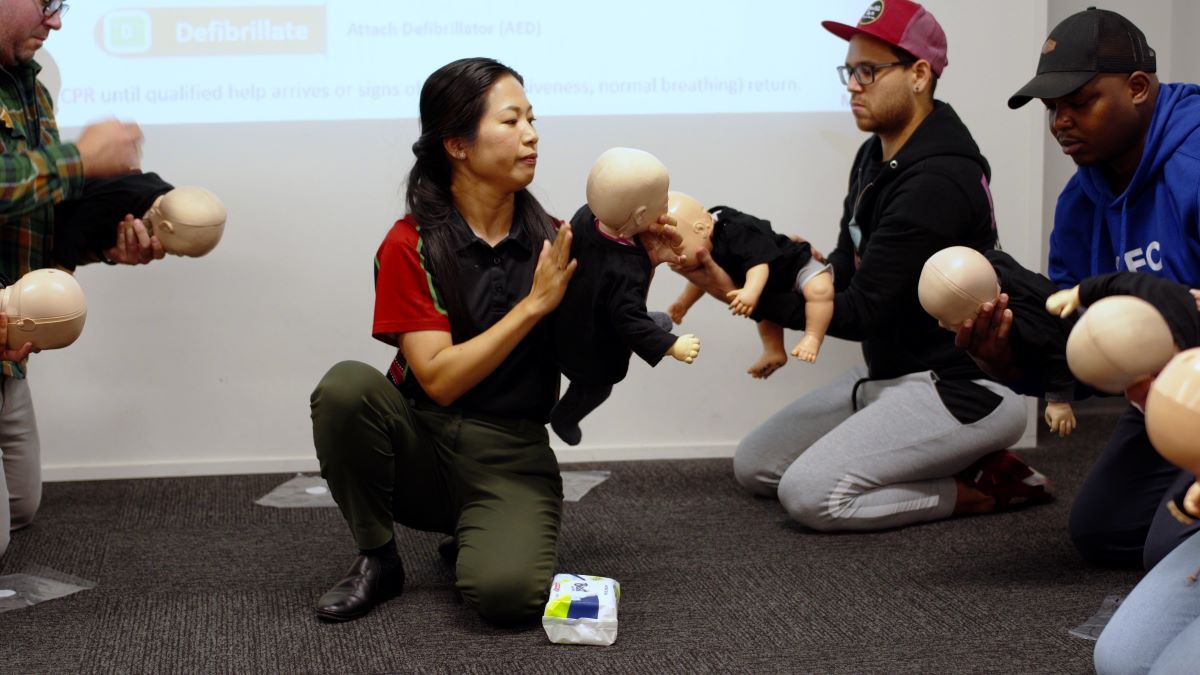
Perform CPR
If the person becomes unconscious at some point and stops breathing, begin CPR. Continue the cycle of chest compression and rescue breathing until medical help arrives.
Conclusion
Insect bites and stings may be painful, frightening, or irritating, but they are rarely a cause for concern. The only time it becomes life-threatening is when the person develops an allergic reaction which can cause swelling in the passageway. This will eventually result in difficulty breathing and airway blockage.
Being prepared for possible emergencies can help you keep yourself and others safe.
For more in-depth information on treating insect bites and stings, enrol in a first aid training course.
Visit our course page to find out more.