Gestational diabetes usually occurs in pregnant women during the course of pregnancy. It is a type of diabetes when the body cannot make enough insulin, causing health problems in both mother and the baby.
While it is not always possible to prevent the condition, there are steps to take that can significantly reduce the risk of having one.
What is Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a temporary condition that occurs only during pregnancy.
About nine in every 100 pregnant women will develop this condition, which can pose a risk during pregnancy and delivery.
A pregnant woman’s cells will become slightly more resistant to insulin. Pregnancy hormones can make it harder for insulin to move glucose from the blood into the body.
All these can cause the amount of glucose or sugar in the mother’s blood to rise, making more nutrients available to the body. However, if the cells become too resistant and glucose cannot reach into them, the blood sugar level will become too high.
High blood sugar can cause health complications for the mother and the growing baby.
Until now, the causes of gestational diabetes are not fully understood, making the condition not entirely preventable. The good news is that there are many ways to lower the risk of the mother developing it.
Keep reading to learn more about the condition and what steps to take to help reduce the risk.
Five Ways to Prevent Gestational Diabetes
Below are five ways to help avoid developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
Eat Wisely
Choosing meals will require more thought for pregnant women. It is essential to pay attention to food intake, including the frequency and schedule.
Consider getting help from a doctor or a registered dietitian in creating a meal plan that is good for both mommy and baby. The goal of the meal plan is to make it easier to keep blood glucose at a healthy level and stays within the range.
Physical Activity
Engaging in mild physical activity can help the body use more glucose, making walking and exercising a good way to help lower sugar levels.
Also, when the body is active, it does not need as much insulin to transport the glucose, making it less insulin resistant.
Lower insulin resistance is a good thing in gestational diabetes.
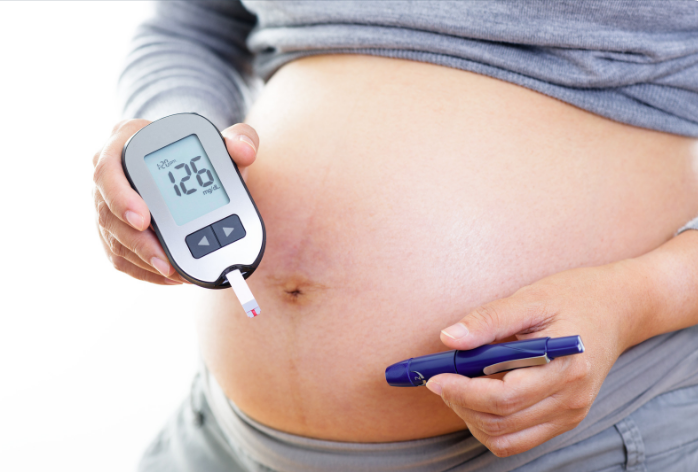
Regular monitoring of blood glucose
Monitoring blood glucose levels throughout the day can help in controlling the condition.
The doctor will explain how to use a blood glucose monitor and detailed instructions on when and how to check the sugar levels often.
Start pregnancy at a healthy weight.
For women planning to get pregnant, losing extra weight beforehand can certainly help have a healthy pregnancy. Focus on making lasting changes, including eating healthy, regular exercise, etc.
While gaining some weight during pregnancy is normal and healthy, gaining too much too quickly is not recommended and can lead to complications.
Attend routine care appointments
See a GP regularly throughout pregnancy for routine care. During the appointments, the doctor may recognise early signs of gestational diabetes and suggest ways to make it preventable.
Will Gestational Diabetes Go Away After I Have the Baby?
Most likely, after the delivery, gestational diabetes will go away. About six weeks after the baby comes out, the doctor will conduct tests to check the blood glucose level to ensure it is within the normal range.
However, because the mother has gestational diabetes, they are at higher risk (33-50%) of having it in yet another pregnancy. There is also a possibility for them to develop Type 2 diabetes.
Understanding First Aid for Gestational Management
There are instances where the mother suffers from diabetic emergencies, which require first aid. If left without treatment, it can lead to something serious.
While gestational diabetes is a cause of concern, the good news is there are ways to prevent complications.
Learn first aid for pregnant women who may be having a diabetic emergency.
With the right help and enough knowledge, it will be a healthy pregnancy and a good start for both mother and the baby.