Sleep is essential to physical and mental health, but many people have difficulty building healthy sleeping habits. A high proportion of the Australian population struggle with poor sleeping practices, which results in constantly feeling tired throughout the day.
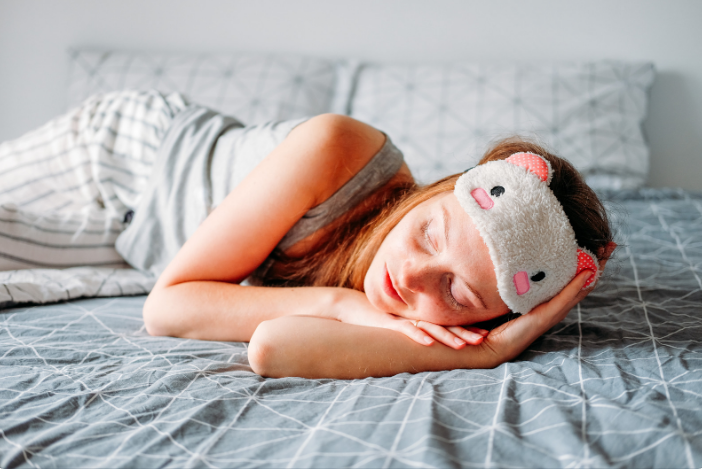
Healthy Sleep Habits
A person’s behaviour throughout the day, especially before bedtime, can significantly impact their sleep. These behaviours can make the difference between a healthy sleep or contributing to one’s sleeplessness.
Lack of sleep (sleep deprivation) can negatively affect one’s health and quality of life. While a few sleepless nights might not bring significant impact, long-term sleep deprivation can result in memory troubles, changes in behaviours, and problems with critical thinking and focusing.
Chronic sleep loss may also result in high blood pressure, weight gain, and a weakened immune system.
Several studies found a connection between chronic poor sleepers and various medical conditions such as cancer. In the research, they studied long-haul flight attendants and nurses who do not get frequent quality sleep to accommodate work shifts and schedules.
In the same research, they have identified various practices and habits that can help maximise their sleeping hours. These practices are called sleep hygiene, which can help even those who struggle with insomnia, jet lag, and frequent changes in the work shift.
Sleep hygiene will help you practice healthy sleeping habits and get the rest you need in this 24/7 modern age.
7 Tips to Build Healthy Sleeping Habits
Follow these healthy sleeping habits if you have difficulty getting enough rest at night or want to improve your sleep.
Set a consistent sleep schedule.
The recommended amount of sleep for a healthy adult is at least seven to eight hours. Set aside time to achieve that ideal amount to be well-rested.
Go to bed on a consistent schedule and get up at the same time every day. Being consistent with your body’s sleep-wake cycle to building healthy sleeping habits.
Eat a healthy diet.
Take your meals two to three hours before bedtime, as consuming solid foods at this time can make it difficult to fall asleep.
Get regular exercise.
Engaging in regular physical exercises can help promote better sleep. However, note that being active too close to bedtime can produce hormones that help prevent falling asleep.
Limit caffeine and avoid nicotine.
Caffeine and nicotine are stimulants keeping you active, even at night. Regular users of these substances may experience withdrawal, leading to restless sleep.
To avoid such, limit coffee intake to one serving a day and do not drink after noon. For tobacco users, quitting smoking can make them sleep faster and better.
Create a restful environment
Keep the room cool, dark, and quiet and avoid exposure to light-emitting screens that might make it more challenging to fall asleep.
Consider using earplugs or calming activities before bedtime (taking a bath, relaxation techniques, etc.) that help promote better sleeping habits.
Keep naps short
Avoid long daytime naps as they interfere with a good night’s sleep. Try limiting these naps to no more than one hour and avoid napping later in the day.
Manage Stress
Take off your mind on worries, concerns, and stress before bedtime. Try to clear your mind and set these things aside for tomorrow.
Stress management can help by starting with the basics, such as getting organised, setting priorities, and delegating tasks. Practising meditation can also help with stress and anxiety.
When to Seek Help
Nearly everyone will experience sleepless nights occasionally. However, if you often have trouble sleeping, it is best to contact a doctor or a sleep specialist.
These health professionals can help you identify and treat the underlying causes that prevent you from getting the best quality sleep.
Learn First Aid
Chronic sleep loss can cause lapses in judgement, trouble with memories, lack of focus, and accidental injuries due to a reduced ability to function.
If you or someone else suffer from sleep loss or sleeping disorder, it is best to learn first aid in case of an accident or injury.